Intersection is a vector overlay operation done by polygon intersection operator. The result of this operator is the collection of all possible polygon intersections; the attribute table result is a join of the two input attribute tables.
Objective: The main objective of this tutorial is to see the houses that would be affected by road expansion project (from Buffer analysis) and to learn intersect in QGIS.
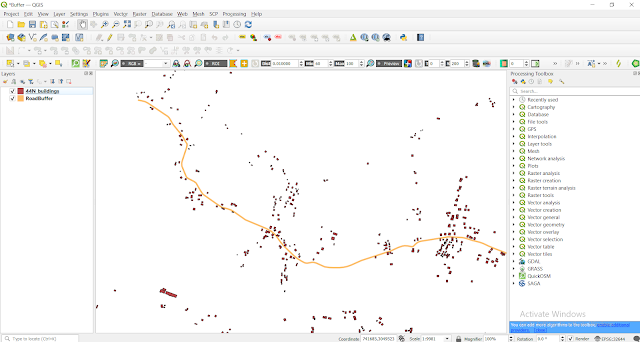
In the last lab we did buffering of road taking distance of ‘5m’. Today we will see the no. of houses that will be affected by this road expansion project using ‘Intersection’ geoprocessing tool.
Using Intersection tool to know the houses affected.
Do the same for ‘RoadBuffer’
You will see something like this.
Step3: Keep Input layer as ‘44N_buildings’, Overlay layer as ‘RoadBuffer’, Save it to a file by clicking three dots icon in (Lab1.5/ Output) with ‘Intersect_RB’ and finally click Run.
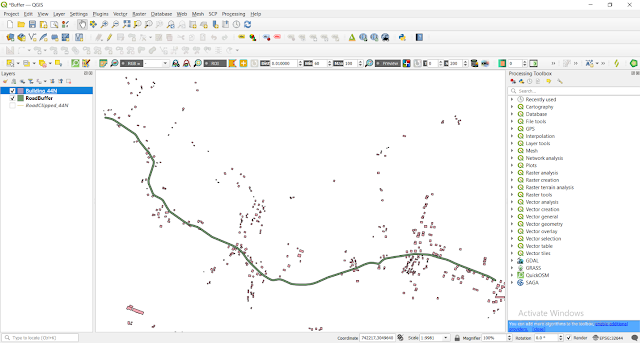
If everything goes right you will see following output.
These are the list of houses that will be affected by the project.